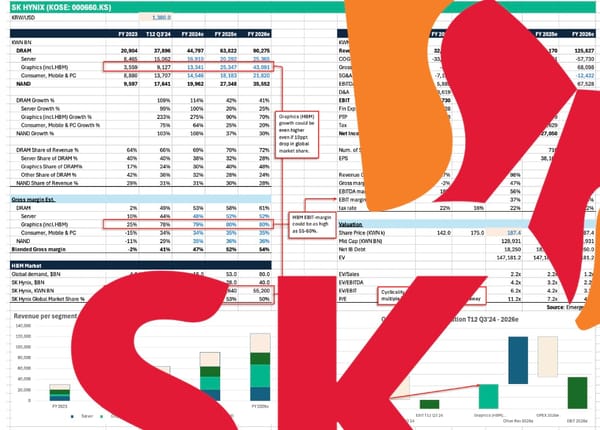
Ever wonder how hackers get malware onto your computer? Here’s the modus that tricks even the most tech savvy
Are you like me, thinking you're too clever and alert to fall for advanced hacking schemes? Think again. Here’s how hackers use sophisticated tactics to slip malware past even the most cautious users—and what you can do to stay safe.
Hackers are constantly evolving, crafting more sophisticated methods to deliver malware without raising the typical red flags. It’s not just about avoiding obvious phishing emails anymore; the game has changed.
1. The Art of Deception: Building Trust Before the Attack
In the more sophisticated schemes, the first step is building a sense of legitimacy. Hackers might reach out through professional channels like LinkedIn, email, or even popular communication platforms like X or Slack, posing as representatives from reputable companies.
You might think you would spot such invites. But even for the most suspiciously minded of us, there are clever ways to lower most people's guard.
Here is a breakdown of the exact method hackers use to gain your trust and bypass your defenses.
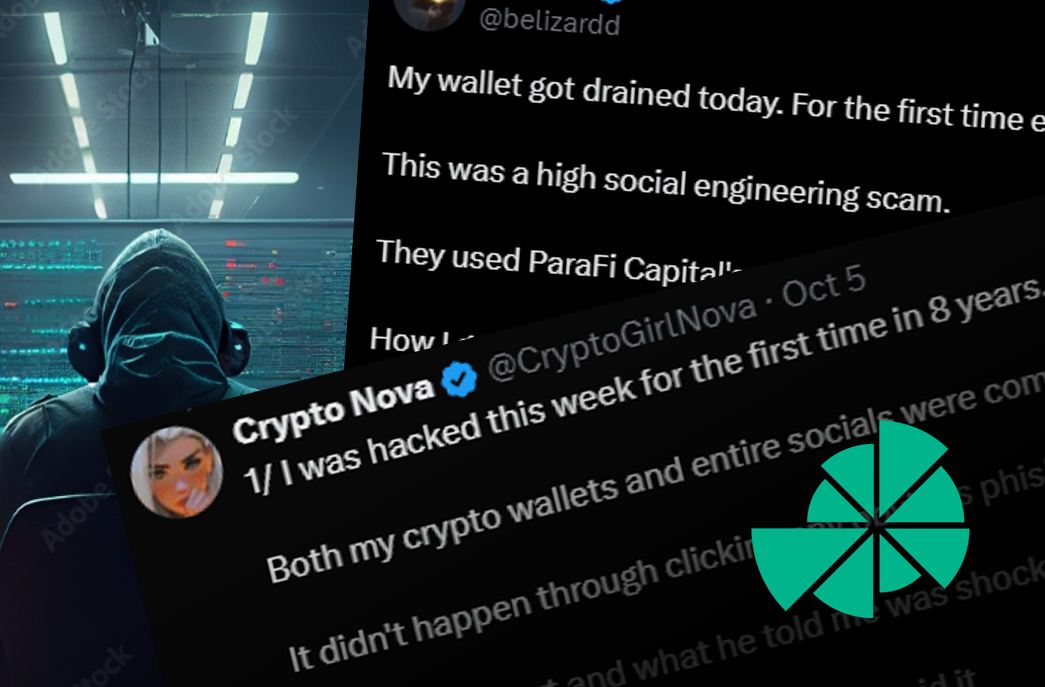
For instance, X user @CryptoGirlNova shared her experience of a sophisticated scam where the hacker posed as a representative from a well-known project, inviting her to a group chat on Slack.
When the shared link failed to work, it seemed like a minor technical issue. This type of approach feels familiar—especially to those accustomed to troubleshooting and technical glitches—making it harder to detect a potential threat.
10/ No red flags here either. Also happens often.
— Crypto Nova (@CryptoGirlNova) October 5, 2024
I friendly told the contact that the link didn't work. It likely expired or it looked like something was wrong with Slack.
He said it was curious. But it happened to some others before. pic.twitter.com/hlvssm1b7D
2. Social Engineering: Exploiting Everyday Scenarios
In the example above, when the Slack link didn’t work, the hacker suggested a solution found on a Reddit thread—a driver update that appeared to fix the issue. This was an actual Reddit thread, with actual comments upvoting is as a functioning solution.
12/ He basically said to update your "Winium drivers"
— Crypto Nova (@CryptoGirlNova) October 5, 2024
To make it more believable, others users upvoted it and actually said it worked (part of the scam ofcourse).
So basically hence I did. pic.twitter.com/J4Y0jI4B0I
These scenarios seem harmless and often mimic legitimate online discussions, giving the victim a false sense of security. What looks like an innocent fix becomes the entry point for malware. It’s a scenario that could catch even experienced professionals off guard.
3. Malware Disguised as Software Fixes
Once the victim is convinced, hackers provide a download link, disguised as a fix or driver update. This malware could be something like a “driver update” that blends in with the usual troubleshooting steps. The malware installs quietly, often without any visible impact at first.
This silent infection is designed to stay hidden until the right moment—often when the victim logs into a sensitive account, enters passwords, or accesses their financial data.
The malware can act as a keylogger, capturing every keystroke, or even access stored authentication information. This is where even the most vigilant users, who think they’ve taken every precaution, can get caught off guard.
4. Advanced Tactics: Persistence Beyond Factory Resets
One of the most concerning aspects of modern malware is its ability to persist even after a factory reset.
Many users believe that a factory reset will wipe all traces of malware, but some advanced threats can attach themselves to a device’s recovery partition. This means that even after resetting your system, the malware can continue to operate, waiting for you to log in again and re-enter your credentials.
In @CryptoGirlNova’s case, a factory reset wasn’t enough to rid her system of the malware that had already infiltrated her computer. When she logged back into her accounts, the damage continued.
5. Why Even Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) Isn’t Foolproof
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is often seen as a gold standard for securing accounts, but it isn’t invincible. Hackers can exploit gaps in 2FA, especially if they’ve compromised the email account linked to the authentication app. This allows them to gain access to the codes and bypass what many see as an impenetrable barrier.
It’s a stark reminder that while 2FA is crucial, it shouldn’t be your only line of defence. Consider additional measures like hardware wallets and physical security keys for critical accounts.
How to Protect Yourself:
- In the case of Crypto, use hardware wallets for sensitive transactions: Hardware wallets remain one of the safest options for storing digital assets. They ensure that even if your device is compromised, your funds are secure as long as your seed phrase is kept offline.
- Be wary of software fixes and driver updates: Always verify the source of any software updates or fixes. If a link points to a lesser-known website or claims to fix a common issue, double-check its validity before downloading anything.
- Separate authentication channels: Keep your authentication apps and email accounts on different devices or accounts. This makes it harder for hackers to gain full control if one of your accounts is compromised.
- Consider a clean installation: If you suspect your system is compromised, a factory reset might not be enough. Consider a complete clean installation of your operating system or using a new device for critical logins.
- Stay informed on new scams: Hackers continually adapt their tactics, so staying up-to-date with the latest cybersecurity threats is crucial.
Conclusion: Don’t Let Overconfidence Be Your Downfall
In a world where cybercriminals are getting more creative, even seasoned professionals can fall victim to cleverly disguised malware.
The best defence is a combination of vigilance, up-to-date knowledge, and robust security practices. Understanding the modern hacker's modus operandi is the first step in protecting yourself, your business, and your digital assets from being compromised.